Commercial-Grade Corner Wall Angles for Heavy-Duty Construction Projects
2025-06-30 04:23:26
I. Introduction: The Essential Need for Corner Protection in Heavy-Duty Buildings
In heavy-duty construction projects such as industrial plants, large commercial complexes, and transportation hubs, corners are critical parts of the building structure that constantly face severe challenges. Frequent collisions from heavy equipment and erosion from complex environments place extremely high demands on corner protection. Commercial-grade corner wall angles made of iron and stainless steel, with their high strength and corrosion resistance, have become core components for ensuring the structural stability of corners and the service life of buildings. This article will provide an in-depth analysis of the industry standards, application要点 (key points), and technological advantages of such corner angles.
II. Analysis of Protection Needs in Heavy-Duty Construction Projects
2.1 Severe Challenges in Construction Environments
On heavy-duty construction sites, large equipment such as forklifts and cranes move around frequently, making corners highly susceptible to violent impacts. High-temperature and high-humidity environments, along with chemical erosion, accelerate the aging of building materials. Long-term exposure to mechanical vibrations and external pressures makes corners a weak link in the building structure.
2.2 Core Performance Indicators for Corner Angles
To cope with complex working conditions, commercial-grade corner wall angles need to possess ultra-high strength and rigidity to resist impact deformation. They should also have excellent corrosion resistance to maintain structural integrity in harsh environments. Additionally, high wear resistance and durability are required to reduce maintenance frequency and lower lifecycle costs.
III. Iron and Stainless Steel: The Foundation of Performance and Application Advantages
3.1 In-Depth Interpretation of Material Properties
Iron Material: With its inherent high strength and rigidity, iron corner angles can effectively absorb impact forces during construction. Through heat treatment processes, their hardness and toughness can be further enhanced. Low-carbon steel, with its strong plasticity, is suitable for complex shaping, while medium-carbon steel, with higher strength, is ideal for heavy-load areas.
Stainless Steel Material: The unique chemical composition of stainless steel endows it with excellent corrosion resistance, performing exceptionally well in humid, acidic, and alkaline environments. Its good oxidation resistance prevents rusting over long-term use. 304 stainless steel offers balanced comprehensive performance, while 316 stainless steel provides even better corrosion resistance, making it suitable for extreme environments.
3.2 Core Advantages in Application Scenarios
Iron and stainless steel corner angles ensure the safety and stability of corners in heavy-duty construction with their high-strength properties, significantly reducing the risk of structural damage. Their corrosion and wear resistance reduce maintenance and replacement costs. Whether in high-temperature workshops, chemical plants, or humid underground spaces, they can consistently provide effective protection.
IV. Industry Standards: The Foundation of Quality Assurance
4.1 Strict Control of Material Standards
At the material level, strict regulations are in place for the chemical composition and impurity content of iron and stainless steel to ensure material purity. Physical performance indicators such as plate thickness, hardness, and tensile strength are also clearly defined to guarantee the quality of corner angles from the source.
4.2 Normative Requirements for Manufacturing Processes
In the forming process, specific technical parameters must be followed during cold rolling and hot rolling to ensure the dimensional accuracy and structural strength of corner angles. In the surface treatment process, strict quality standards exist for processes such as galvanizing, polishing, and passivation to enhance rust, wear, and aesthetic performance.
4.3 Authoritative Standards for Performance Testing
Through simulated actual collision scenarios, impact resistance tests are conducted to set qualified indicators. Corrosion resistance tests are carried out in different corrosive environments to assess product adaptability based on established procedures. Meanwhile, strict inspections are conducted on the dimensional tolerances and geometric tolerances of corner angles to ensure product consistency.
V. Construction and Installation: Standardized Processes Ensure Protective Efficiency
5.1 Rigorous Preparation Before Construction
Before construction, comprehensive quality inspections of corner angles are required, including verification of material certificates, performance reports, and appearance quality. Meanwhile, the corner base should be treated to ensure a flat and clean surface, laying a foundation for installation.
5.2 Standardized Operation of Installation Processes
When cutting iron and stainless steel corner angles, specialized tools should be used to control cutting accuracy. Fixing methods, such as bolt anchoring, welding, or bonding, should be selected based on scenarios, with clear operating specifications for each method. Appropriate sealing materials should be used at joints, and gap widths should be strictly controlled to ensure waterproofing, dustproofing, and structural stability.
5.3 Strict Inspection During Acceptance
During acceptance, the surface finish of corner angles should be checked to ensure no deformation or damage. Professional equipment should be used to detect fixing firmness. Waterproofing and rust-proofing treatments should be carefully inspected to ensure they meet protection requirements.
VI. Application Strategies in Diverse Scenarios
6.1 Protection Solutions for Industrial Plants
In high mechanical activity areas, thickened corner angles with reinforced fixing should be used to enhance impact resistance. In chemically corrosive environments, stainless steel models with strong corrosion resistance should be precisely selected to ensure long-term stability of corners.
6.2 Design Key Points for Commercial Complexes
In public areas, the specifications of anti-collision corner angles should be designed based on foot traffic to ensure safety. Meanwhile, a balance between aesthetics and strength should be achieved through surface treatment processes to integrate with the overall spatial design.
6.3 Reinforcement Measures for Transportation Hubs
For scenarios with high foot traffic and frequent handling, wear-resistant and scratch-resistant stainless steel corner angles should be used, combined with special installation techniques to maintain protective performance over long-term use.
VII. Maintenance and Care: The Key to Extending Service Life
7.1 Specification for Routine Inspections
Scientific inspection cycles should be established to regularly check key parts such as joints, fixing points, and surface coatings, promptly identifying potential issues.
7.2 Standardized Process for Problem Handling
For minor wear and rust, professional materials should be used for repair. When corner angles are severely damaged, strict replacement procedures should be followed, and quality acceptance should be conducted to ensure new corner angles meet standards.
VIII. Technological Innovation: New Trends in Industry Development
8.1 Direction of Material Innovation
The research and development of new high-strength iron alloy materials are continuously advancing, aiming to further enhance the performance of corner angles. Stainless steel materials are continuously breaking through in corrosion resistance technology, expanding application boundaries.
8.2 Upgrade of Manufacturing and Construction
Automated production processes improve the manufacturing precision and efficiency of corner angles. Intelligent installation equipment and technologies reduce human errors, driving the industry towards high efficiency and precision.
IX. Conclusion: Upholding Standards to Safeguard Heavy-Duty Building Quality
Iron and stainless steel commercial-grade corner wall angles, with their strict standard system and excellent performance, have become indispensable protective barriers for heavy-duty construction projects. From material selection to construction acceptance, from daily maintenance to technological innovation, every aspect is crucial for building safety and quality. Adhering to standards and applying them scientifically can fortify corner defenses in heavy-duty buildings and promote high-quality development in the industry.
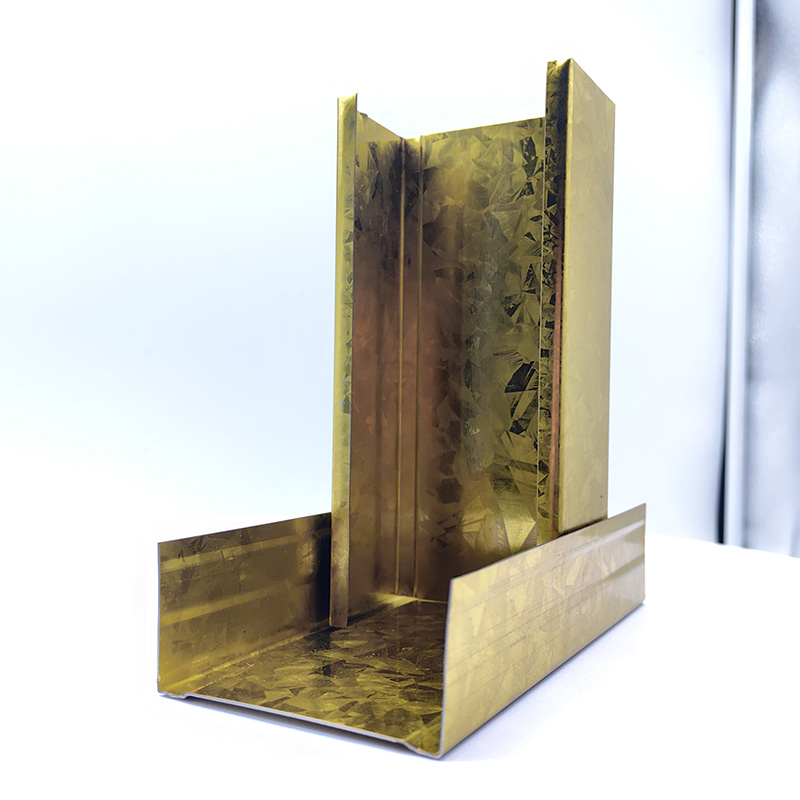
A Double Anti-Rust Gold Partition Wall Stud is a type of steel stud commonly used in the co...
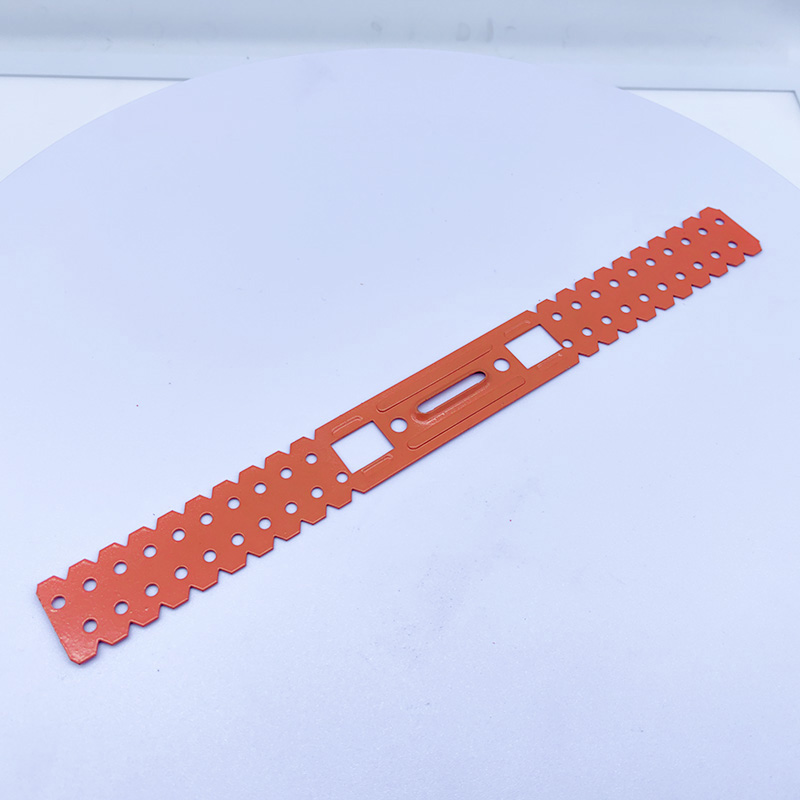
A CD UD Profile Furring Clip U Clamp is a type of metal fastening component used in the ins...

A 60mm Ceiling Grid refers to a type of suspended ceiling system, commonly used in commerci...
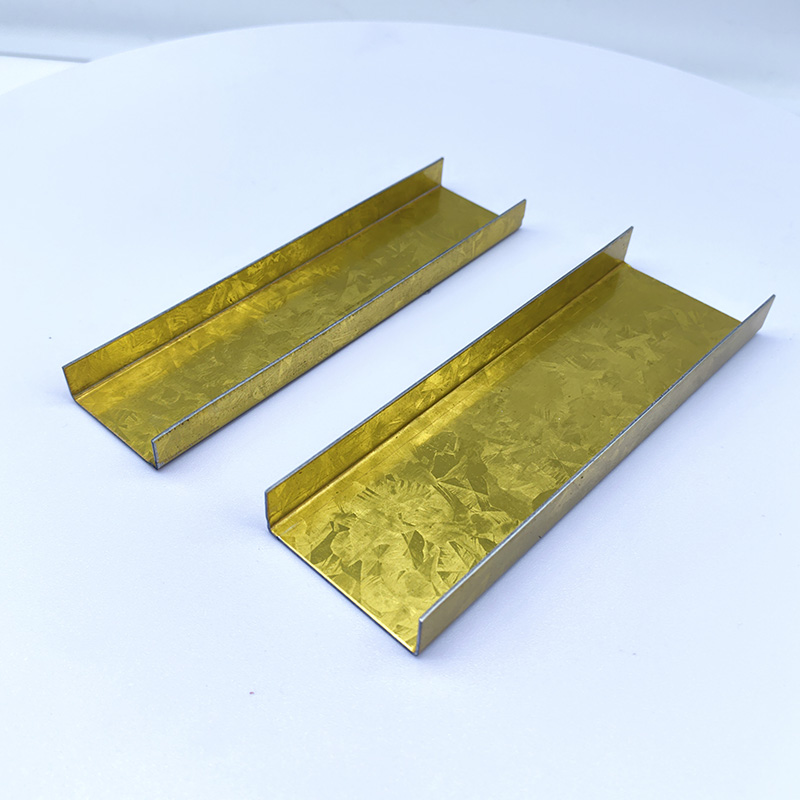
38mm Main Tee and 50mm Main Tee refer to the widths of the main tee profiles used in suspen...

